Cancer is a disease of cells where some cells in a body start to grow uncontrollably and can then spread to other parts of the body. This may not sound serious since it is only cells that are replicating uncontrollably, but cancer is one of the top few lethal diseases out there in the world, causing around 10 million deaths each year. In the human body, everything has its purpose, or you can say that each cell is designed to do a particular job, and they stay in a particular type of body part for their entire existence. However, in the case of cancer, these cells start to grow and multiply within that body part. In the next stage, these cells can travel from one body part to the other and form tumors in other parts of the body. There are multiple treatments for cancer, but the most common types of treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
What is Radiation Therapy?
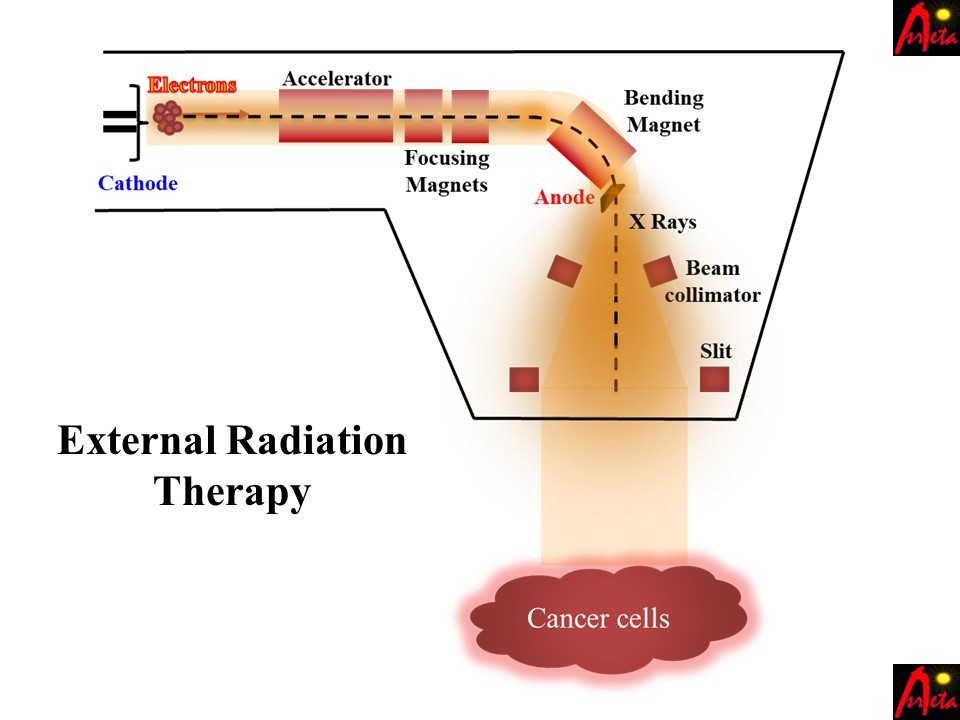
The type of cancer treatment may vary depending on the location of cancer. Therefore, depending on the size and locale of the cancerous area, radiation therapy can also be divided into two further categories. These two categories are external radiation therapy and internal radiation therapy. In external radiation therapy, an ionizing beam of x-rays is bombarded on the cancerous area to kill the cancer cells or suppress their growth. External radiation therapy is location-dependent since the machine that generates the radiation focuses on a single part of the body. However, the machine producing x-rays can move around you to cover any other area affected by cancer. A schematic of external radiation therapy is given in Figure 1. Figure 1 shows that in external radiation therapy, electrons are accelerated through an accelerator and then focussed by magnets onto the cathode, where x-rays are generated. These x-rays are then focused on the cancer cells or cancerous areas of the body.
In internal radiation therapy, a radioactive material is placed inside the body. This material can be in the form of a solid, or it can be in the form of a liquid. Where the radiation material is solid, the material is placed near the cancerous area to eliminate or suppress the growth, whereas, for liquid radiation material, the liquid is injected or swallowed, upon which the liquid will travel through the blood and tissues to eliminate the cancerous cells.
Side effects of radiation therapy
Since this therapy requires the use of x-rays (electromagnetic waves having high energy), prolonged exposure can be harmful to human beings. Doses of radiation vary for various types of cancer treatment. Apart from this, the radiation does not distinguish between cancer cells and normal cells, and both cells get damaged or eliminated in the area exposed to the radiation. To reduce the side effects of radiation therapy, usually, radioprotective drugs are given to the patients before treatment. The success rate of radiotherapy is around 90% when the cancer is in its early stages.
Further reading
If you liked this post, the following posts might interest you further.
- Construction, working, and new technologies of OLED TV
- Laser and its applications in medicine and technology
- LED light, its construction, types and colors, power, life, and technology
- Optical fiber design and applications
- Radiation therapy for cancer treatment and its side effects
