A mirror is a reflecting surface that reflects light excellently and does not allow it to refract, producing a clear image. It produces either real or virtual images. A famous German chemist Justus made mirrors commercially available in 1835. He made the mirror by coating a thin layer of silver onto the glass surface employing a chemical reaction.
Plane mirror
The most common mirrors are plane mirrors which are absolutely flat. These are made by putting some excellent reflective substance like silver nitrate onto a piece of glass. When we place an object in front of a plane mirror, an image is formed by reflection. The source object produces an incident ray that bounces back. The plane mirror produces an upright virtual image. It makes an erect image which means that the size of the image is the same as that of the real object. A virtual image is an image that forms on the opposite side of the mirror, apparently. The image created where the ray of the light seems to diverge. The virtual image is upright and appears to have an equal distance from the actual object. A virtual image is formed by the diverging lens (concave lens), convex mirror, or plane mirror. The rays do not actually converge, so a virtual image cannot be obtained onto the screen.
A virtual image seems to be on the mirror or lens. Although plane mirrors produce virtual images that we have discussed in some detail, there are some more important characteristics to consider. One of which is the orientation of the image made by a plane mirror. When we stand in front of a plane mirror, we note a left-right reversal of image, i.e., when we raise our right hand, it looks like our left hand in the mirror, and when we raise our left hand, it looks like to be our right hand. The same thing happens when some alphabets are placed in front of a plane mirror, i.e., the word “apple” looks like” elppa” in the mirror. This is due to a change in the frame of reference. If your t-shirt is made transparent and has a printed word having alphabets, the printed word will be looking in reverse order when it will be seen from the backside of the shirt. The same happens for the plane mirror. It is all due to a change in the frame of reference.
Convex mirror
Now we talk about curved/spherical mirrors. Spherical Mirrors have two types. One is the concave mirror, and the second is the convex mirror. First, we talk about the convex mirror, which is also called a diverging mirror. Sometimes it is called a fish mirror. The reflective surface of the convex mirror is slightly extended towards the source of light. A convex mirror can reflect all rays falling on it in the outward direction. It produces a virtual image. The size of the image is smaller than the actual object. So it is used where we have to see a broader view in the mirror. In image formation by a convex mirror, there is a single point on which all the rays from the outside meet. The point is called the focal point, and the distance between the mirror and that point is called the focal length (F) of the mirror. It is different for various mirrors.
A virtual image is formed because the center of curvature and focus point is imaginary and cannot be reached. It means that the image formed by a convex mirror cannot be projected on the real screen. The image produced is upright and always smaller than the actual size of the object. When the object lies at infinity, a tiny image is formed at the focus point, it will be diminished and erect. Interestingly, our eyes have a convex lens, and its outer surface acts slightly like a convex mirror.
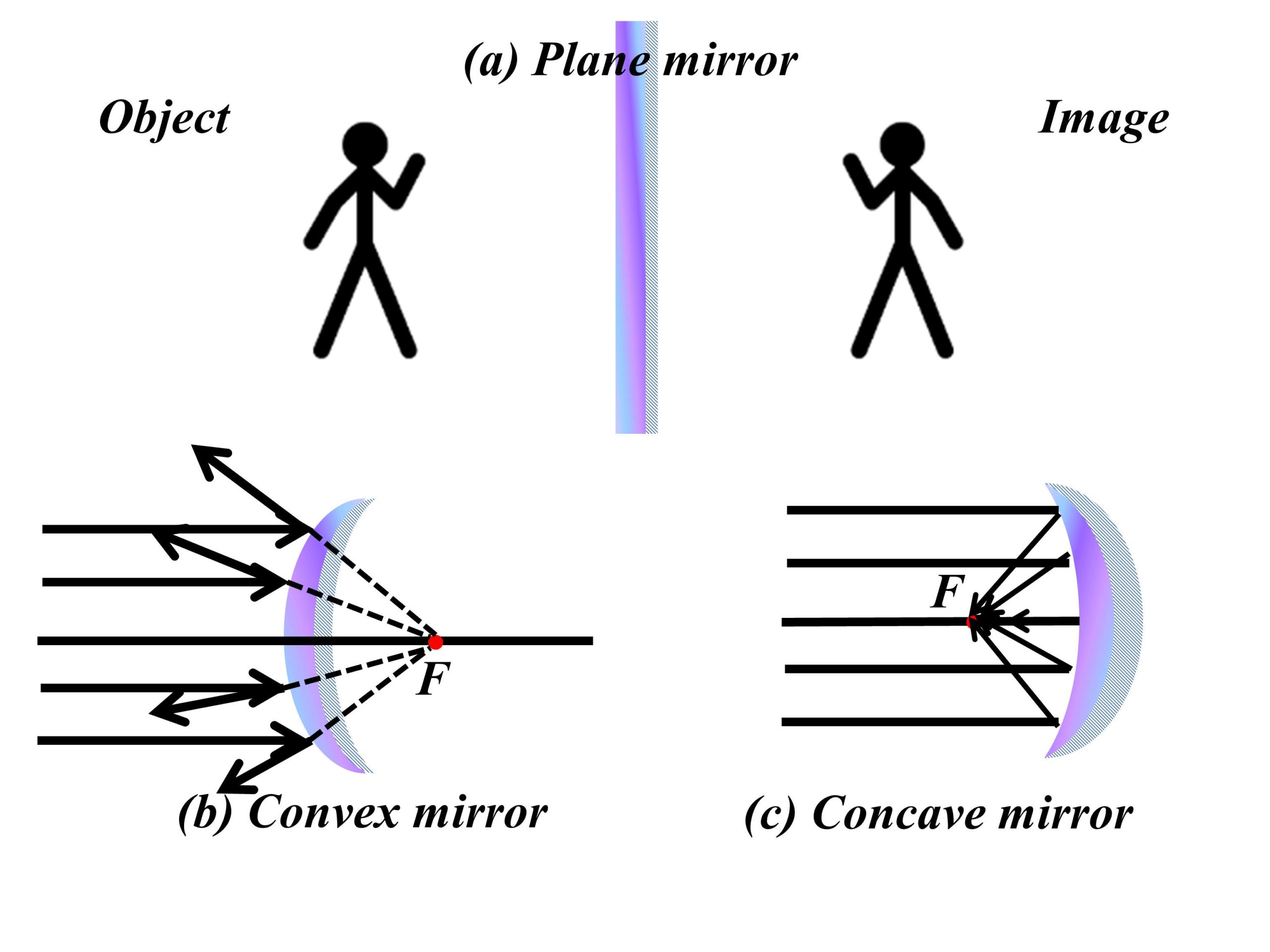
Concave mirror
Now we discuss the concave mirror. It is a mirror that is bent inside at its center. It looks like a cave. The law of reflection also holds for the concave mirror, but the angle of incidence is not equal to the angle of reflection. A concave mirror can produce a real or virtual image in front of it at its point of focus. The image looks like a floating image in the air. The focal length of the concave mirror is half of its radius. If the object is in between the focus and the mirror, the image will be virtual and bigger than the actual. The orientation will be the same as the object. If the object is in between focus and the mirror’s center, the image will be real, large, and inverted. If the object lies at a distance equal to double its focal length, the image will be real and inverted. Also, the image will be smaller in size. If an object is placed at infinity, the image will be real and very small and will be at the focus point. If an object is beyond the center of curvature, the image will be real, small, and inverted. It will be between the center of curvature and the focus point.
Applications of mirrors
Plane mirror applications
A plane mirror is used in kaleidoscopes. A pattern of various colors is produced with plane mirrors and color glass. Plane mirrors are also used in periscopes which are widely used in submarines. In periscope, a plane mirror reflects all images of nearby ships. In automobiles, plane mirrors have a very vital role. They are used in headlights to reflect parallel rays of light in a straight line. Convex mirrors are used as side mirrors in vehicles because they form erect images and cover wider views. Plane mirrors are also used in flashlights and torches to give the source light a straight path. The same purpose they serve in projectors. In our homes plane mirrors are used by all the persons. They are used in brushing, shaving, and makeup. Plane mirrors are used by a dentist to see the inside of the mouth. They are also used in microscopes to reflect the beam of light. Plane mirrors are used in solar cookers because they excellently reflect solar rays. Plane mirrors are also used for security purposes in big shops.
Convex mirror applications
Convex mirrors are used as side mirrors in vehicles because they form erect images and cover wider views. They give a larger view as compared to plane mirrors. They are used in building hallways and in shops. In shops, security personnel can examine a broader view of his shop and see that side that is not visible by the naked eye. In sharp turns of mountainous roads, they are fixed at the corner to see the other side of the road. These mirrors are also employed in parking lots to make taking out cars easily. They are also used in automatic teller machines for the user’s security point of view, i.e., a user can see his backside while entering his pin. They are also used in sunglasses to reflect all the rays coming from the sun. They are also used in magnifying glasses. Two convex mirrors placed back to back produce a magnified image. They are used in street lights to reflect light on the road.
Concave mirror applications
Finally, we discuss the applications of a concave mirror. In observational astronomy, concave mirrors are used in reflecting telescopes. Concave mirror in reflecting telescopes collects light from distant universal objects because these objects are very far away, so their rays of light are nearly parallel. The concave mirrors focus the light rays on a plane mirror which is placed at its focal length. As we know, that concave mirror converges light, so the intensity of incoming rays increases on a plane mirror. Then the reflection from a plane mirror is seen by an eyepiece. A concave mirror is also used in microscopes as a condenser. Light from the external source is directed to the object under consideration. The concave mirror then focuses that light on that object to examine it clearly. The orientation of the concave mirror can also be varied according to requirements. Concave mirrors are also used in headlights and in torches. The bulb of the source light is placed at the focal length of the concave mirror. The light coming from a source is changed into parallel rays after reflecting from a concave mirror. The reflected rays can cover more distance with high intensity.
Concave mirrors have very crucial applications in medical instruments. They are used in ophthalmoscopes (to test human eyes), otoscopes (to examine ears), and many more. They are extensively used by head mirrors in the instruments of ENT specialists. The main purpose in all these applications is to provide focused and intense light to the organ under examination. Dentists also use concave mirrors to examine the internal of the mouth, whose image is magnified by the concave mirror. They are also used in optical cavities, which is the subject of laser physics. The rays of light are reflected many times inside the cavity to form standing waves. Concave mirrors are used in solar furnaces. The concave mirror collects sun rays and focuses them on its focal point. It is utilized for heating, melting metals, generating electricity, and cooking food. They are also used in satellite dishes and in visual bomb detectors. Concave mirrors can enlarge or shrink the image according to the distance from an object so they are used in sensitive devices.
Further readings
If you liked this post you might be interested in reading the following posts.
- Construction, working, and new technologies of OLED TV

- Laser and its applications in medicine and technology
- LED light, its construction, types and colors, power, life, and technology
- Optical fiber design and applications
- Radiation therapy for cancer treatment and its side effects

